Added test flags for - redis address (defaults to "localhost:6379") - redis db number (defaults to 14) - log level (defaults to FATAL)
Asynq
Overview
Asynq is a Go library for queueing tasks and processing them in the background with workers. It is backed by Redis and it is designed to have a low barrier to entry. It should be integrated in your web stack easily.
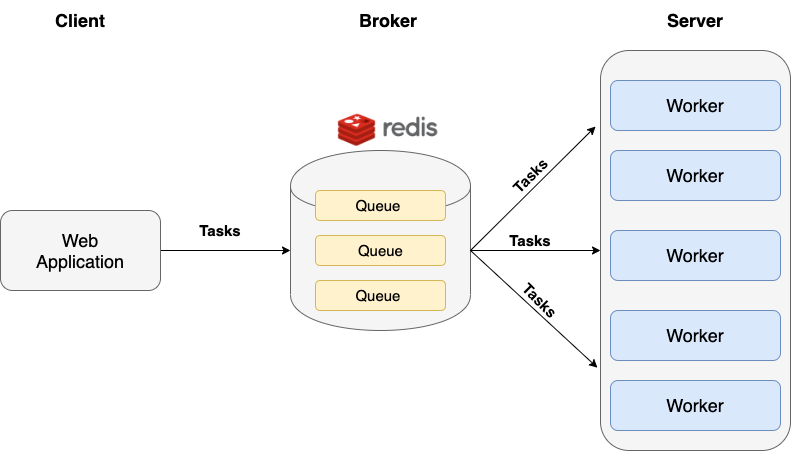
Highlevel overview of how Asynq works:
- Client puts task on a queue
- Server pulls task off queues and starts a worker goroutine for each task
- Tasks are processed concurrently by multiple workers
Task queues are used as a mechanism to distribute work across multiple machines.
A system can consist of multiple worker servers and brokers, giving way to high availability and horizontal scaling.
Stability and Compatibility
Important Note: Current major version is zero (v0.x.x) to accomodate rapid development and fast iteration while getting early feedback from users (Feedback on APIs are appreciated!). The public API could change without a major version update before v1.0.0 release.
Status: The library is currently undergoing heavy development with frequent, breaking API changes.
Features
- Guaranteed at least one execution of a task
- Scheduling of tasks
- Durability since tasks are written to Redis
- Retries of failed tasks
- Weighted priority queues
- Strict priority queues
- Low latency to add a task since writes are fast in Redis
- De-duplication of tasks using unique option
- Allow timeout and deadline per task
- Flexible handler interface with support for middlewares
- Support Redis Sentinels for HA
- CLI to inspect and remote-control queues and tasks
Quickstart
First, make sure you are running a Redis server locally.
$ redis-server
Next, write a package that encapsulates task creation and task handling.
package tasks
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/hibiken/asynq"
)
// A list of task types.
const (
EmailDelivery = "email:deliver"
ImageProcessing = "image:process"
)
//--------------------------------------------
// Write function NewXXXTask to create a task.
//--------------------------------------------
func NewEmailDeliveryTask(userID int, tmplID string) *asynq.Task {
payload := map[string]interface{}{"user_id": userID, "template_id": tmplID}
return asynq.NewTask(EmailDelivery, payload)
}
func NewImageProcessingTask(src, dst string) *asynq.Task {
payload := map[string]interface{}{"src": src, "dst": dst}
return asynq.NewTask(ImageProcessing, payload)
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------
// Write function HandleXXXTask to handle the given task.
// NOTE: It satisfies the asynq.HandlerFunc interface.
//
// Handler doesn't need to be a function. You can define a type
// that satisfies asynq.Handler interface. See example below.
//-------------------------------------------------------------
func HandleEmailDeliveryTask(ctx context.Context, t *asynq.Task) error {
userID, err := t.Payload.GetInt("user_id")
if err != nil {
return err
}
tmplID, err := t.Payload.GetString("template_id")
if err != nil {
return err
}
fmt.Printf("Send Email to User: user_id = %d, template_id = %s\n", userID, tmplID)
// Email delivery logic ...
return nil
}
type ImageProcesser struct {
// ... fields for struct
}
// ImageProcessor implements asynq.Handler.
func (p *ImageProcessor) ProcessTask(ctx context.Context, t *asynq.Task) error {
src, err := t.Payload.GetString("src")
if err != nil {
return err
}
dst, err := t.Payload.GetString("dst")
if err != nil {
return err
}
fmt.Printf("Process image: src = %s, dst = %s\n", src, dst)
// Image processing logic ...
return nil
}
func NewImageProcessor() *ImageProcessor {
// ... return an instance
}
In your web application code, import the above package and use Client to put tasks on the queue.
A task will be processed asynchronously by a background worker as soon as the task gets enqueued.
Scheduled tasks will be stored in Redis and will be enqueued at the specified time.
package main
import (
"time"
"github.com/hibiken/asynq"
"your/app/package/tasks"
)
const redisAddr = "127.0.0.1:6379"
func main() {
r := asynq.RedisClientOpt{Addr: redisAddr}
c := asynq.NewClient(r)
defer c.Close()
// ----------------------------------------------------
// Example 1: Enqueue task to be processed immediately.
// Use (*Client).Enqueue method.
// ----------------------------------------------------
t := tasks.NewEmailDeliveryTask(42, "some:template:id")
err := c.Enqueue(t)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("could not enqueue task: %v", err)
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------
// Example 2: Schedule task to be processed in the future.
// Use (*Client).EnqueueIn or (*Client).EnqueueAt.
// ----------------------------------------------------------
t = tasks.NewEmailDeliveryTask(42, "other:template:id")
err = c.EnqueueIn(24*time.Hour, t)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("could not schedule task: %v", err)
}
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example 3: Set options to tune task processing behavior.
// Options include MaxRetry, Queue, Timeout, Deadline, Unique etc.
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------
c.SetDefaultOptions(tasks.ImageProcessing, asynq.MaxRetry(10), asynq.Timeout(time.Minute))
t = tasks.NewImageProcessingTask("some/blobstore/url", "other/blobstore/url")
err = c.Enqueue(t)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("could not enqueue task: %v", err)
}
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Example 4: Pass options to tune task processing behavior at enqueue time.
// Options passed at enqueue time override default ones, if any.
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------
t = tasks.NewImageProcessingTask("some/blobstore/url", "other/blobstore/url")
err = c.Enqueue(t, asynq.Queue("critical"), asynq.Timeout(30*time.Second))
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("could not enqueue task: %v", err)
}
}
Next, create a worker server to process these tasks in the background.
To start the background workers, use Server and provide your Handler to process the tasks.
You can optionally use ServeMux to create a handler, just as you would with "net/http" Handler.
package main
import (
"log"
"github.com/hibiken/asynq"
"your/app/package/tasks"
)
const redisAddr = "127.0.0.1:6379"
func main() {
r := asynq.RedisClientOpt{Addr: redisAddr}
srv := asynq.NewServer(r, asynq.Config{
// Specify how many concurrent workers to use
Concurrency: 10,
// Optionally specify multiple queues with different priority.
Queues: map[string]int{
"critical": 6,
"default": 3,
"low": 1,
},
// See the godoc for other configuration options
})
// mux maps a type to a handler
mux := asynq.NewServeMux()
mux.HandleFunc(tasks.EmailDelivery, tasks.HandleEmailDeliveryTask)
mux.Handle(tasks.ImageProcessing, tasks.NewImageProcessor())
// ...register other handlers...
if err := srv.Run(mux); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("could not run server: %v", err)
}
}
For a more detailed walk-through of the library, see our Getting Started Guide.
To Learn more about asynq features and APIs, see our Wiki and godoc.
Command Line Tool
Asynq ships with a command line tool to inspect the state of queues and tasks.
Here's an example of running the stats command.
For details on how to use the tool, refer to the tool's README.
Installation
To install asynq library, run the following command:
go get -u github.com/hibiken/asynq
To install the CLI tool, run the following command:
go get -u github.com/hibiken/asynq/tools/asynq
Requirements
| Dependency | Version |
|---|---|
| Redis | v2.8+ |
| Go | v1.13+ |
Contributing
We are open to, and grateful for, any contributions (Github issues/pull-requests, feedback on Gitter channel, etc) made by the community. Please see the Contribution Guide before contributing.
Acknowledgements
- Sidekiq : Many of the design ideas are taken from sidekiq and its Web UI
- RQ : Client APIs are inspired by rq library.
- Cobra : Asynq CLI is built with cobra
License
Asynq is released under the MIT license. See LICENSE.