Asynq CLI
Asynq CLI is a command line tool to monitor the tasks managed by asynq package.
Table of Contents
Installation
In order to use the tool, compile it using the following command:
go get github.com/hibiken/asynq/tools/asynq
This will create the asynq executable under your $GOPATH/bin directory.
Quickstart
The tool has a few commands to inspect the state of tasks and queues.
Run asynq help to see all the available commands.
Asynq CLI needs to connect to a redis-server to inspect the state of queues and tasks. Use flags to specify the options to connect to the redis-server used by your application.
By default, CLI will try to connect to a redis server running at localhost:6379.
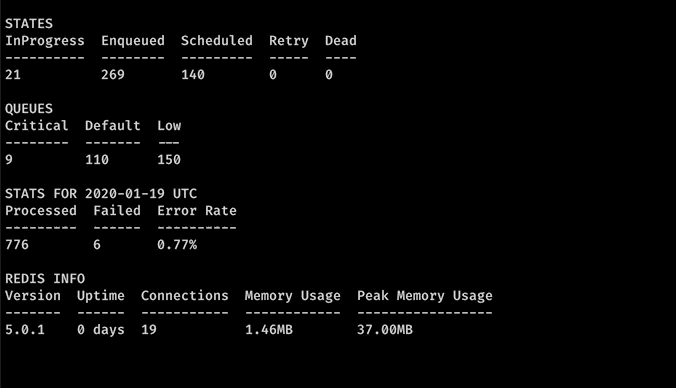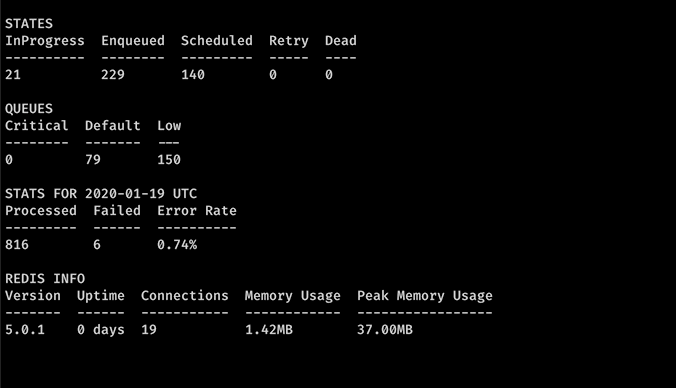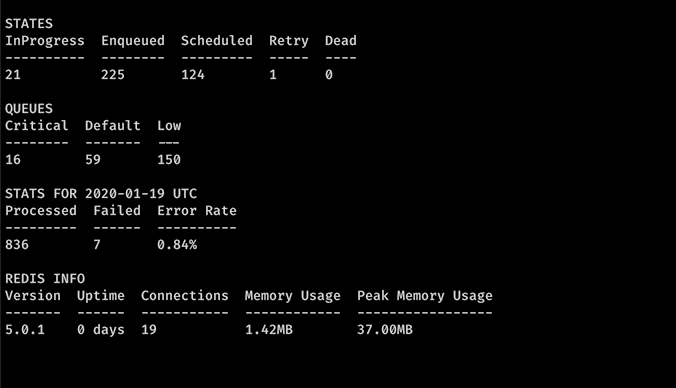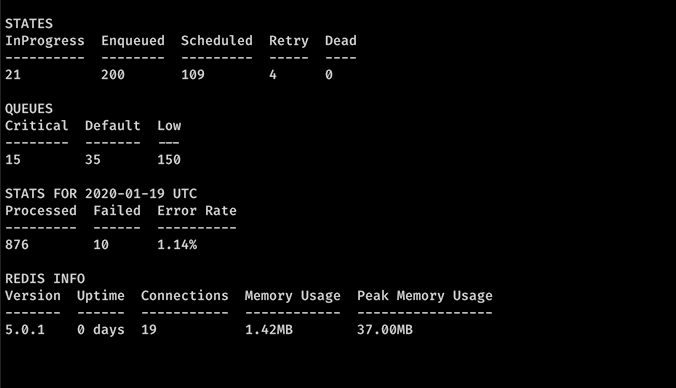
Stats
Stats command gives the overview of the current state of tasks and queues. You can run it in conjunction with watch command to repeatedly run stats.
Example:
watch -n 3 asynq stats
This will run asynq stats command every 3 seconds.
History
History command shows the number of processed and failed tasks from the last x days.
By default, it shows the stats from the last 10 days. Use --days to specify the number of days.
Example:
asynq history --days=30
Servers
Servers command shows the list of running worker servers pulling tasks from the given redis instance.
Example:
asynq servers
List
List command shows all tasks in the specified state in a table format
Example:
asynq ls retry
asynq ls scheduled
asynq ls dead
asynq ls enqueued:default
asynq ls inprogress
Enqueue
There are two commands to enqueue tasks.
Command enq takes a task ID and moves the task to Enqueued state. You can obtain the task ID by running ls command.
Example:
asynq enq d:1575732274:bnogo8gt6toe23vhef0g
Command enqall moves all tasks to Enqueued state from the specified state.
Example:
asynq enqall retry
Running the above command will move all Retry tasks to Enqueued state.
Delete
There are two commands for task deletion.
Command del takes a task ID and deletes the task. You can obtain the task ID by running ls command.
Example:
asynq del r:1575732274:bnogo8gt6toe23vhef0g
Command delall deletes all tasks which are in the specified state.
Example:
asynq delall retry
Running the above command will delete all Retry tasks.
Kill
There are two commands to kill (i.e. move to dead state) tasks.
Command kill takes a task ID and kills the task. You can obtain the task ID by running ls command.
Example:
asynq kill r:1575732274:bnogo8gt6toe23vhef0g
Command killall kills all tasks which are in the specified state.
Example:
asynq killall retry
Running the above command will move all Retry tasks to Dead state.
Cancel
Command cancel takes a task ID and sends a cancelation signal to the goroutine processing the specified task.
You can obtain the task ID by running ls command.
The task should be in "in-progress" state. Handler implementation needs to be context aware in order to actually stop processing.
Example:
asynq cancel bnogo8gt6toe23vhef0g
Pause
Command pause pauses the spcified queue. Tasks in paused queues are not processed by servers.
To resume processing from the queue, use unpause command.
To see which queues are currently paused, use stats command.
Example:
asynq pause email
asynq unpause email
Config File
You can use a config file to set default values for the flags. This is useful, for example when you have to connect to a remote redis server.
By default, asynq will try to read config file located in
$HOME/.asynq.(yaml|json). You can specify the file location via --config flag.
Config file example:
uri: 127.0.0.1:6379
db: 2
password: mypassword
This will set the default values for --uri, --db, and --password flags.