Asynq CLI
Asynq CLI is a command line tool to monitor the tasks managed by asynq package.
Table of Contents
Installation
In order to use the tool, compile it using the following command:
go get github.com/hibiken/asynq/tools/asynq
This will create the asynq executable under your $GOPATH/bin directory.
Quickstart
The tool has a few commands to inspect the state of tasks and queues.
Run asynq help to see all the available commands.
Asynq CLI needs to connect to a redis-server to inspect the state of queues and tasks. Use flags to specify the options to connect to the redis-server used by your application.
By default, CLI will try to connect to a redis server running at localhost:6379.
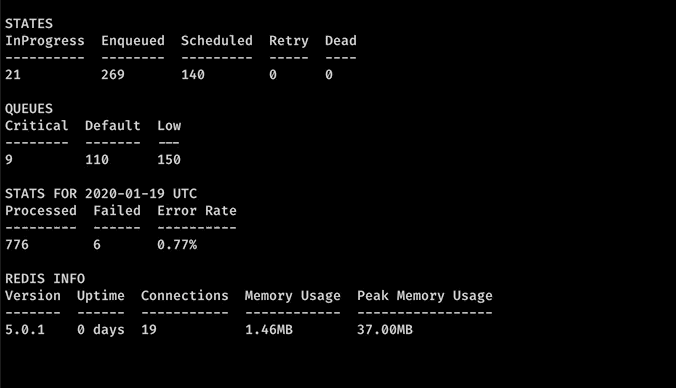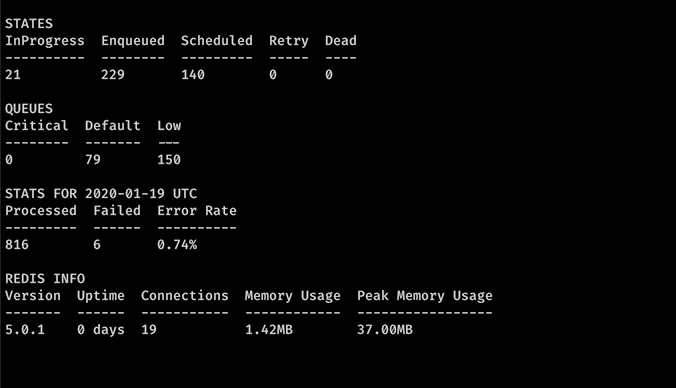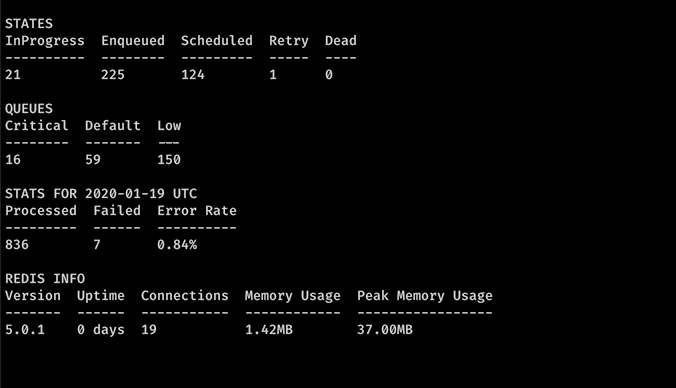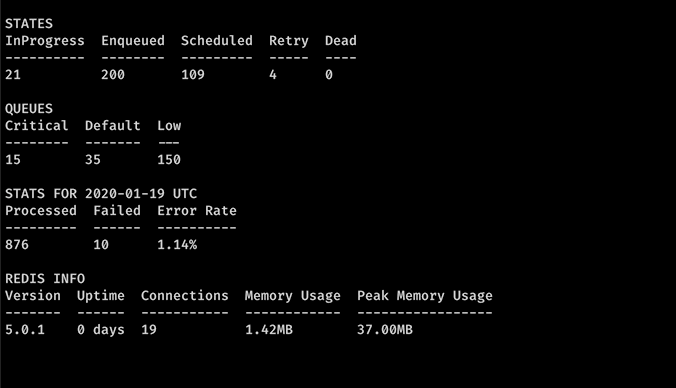
Stats
Stats command gives the overview of the current state of tasks and queues. You can run it in conjunction with watch command to repeatedly run stats.
Example:
watch -n 3 asynq stats
This will run asynq stats command every 3 seconds.
History
History command shows the number of processed and failed tasks from the last x days.
By default, it shows the stats from the last 10 days. Use --days to specify the number of days.
Example:
asynq history --days=30
Servers
Servers command shows the list of running worker servers pulling tasks from the given redis instance.
Example:
asynq servers
List
List command shows all tasks in the specified state in a table format
Example:
asynq ls retry
asynq ls scheduled
asynq ls dead
asynq ls enqueued:default
asynq ls inprogress
Enqueue
There are two commands to enqueue tasks.
Command enq takes a task ID and moves the task to Enqueued state. You can obtain the task ID by running ls command.
Example:
asynq enq d:1575732274:bnogo8gt6toe23vhef0g
Command enqall moves all tasks to Enqueued state from the specified state.
Example:
asynq enqall retry
Running the above command will move all Retry tasks to Enqueued state.
Delete
There are two commands for task deletion.
Command del takes a task ID and deletes the task. You can obtain the task ID by running ls command.
Example:
asynq del r:1575732274:bnogo8gt6toe23vhef0g
Command delall deletes all tasks which are in the specified state.
Example:
asynq delall retry
Running the above command will delete all Retry tasks.
Kill
There are two commands to kill (i.e. move to dead state) tasks.
Command kill takes a task ID and kills the task. You can obtain the task ID by running ls command.
Example:
asynq kill r:1575732274:bnogo8gt6toe23vhef0g
Command killall kills all tasks which are in the specified state.
Example:
asynq killall retry
Running the above command will move all Retry tasks to Dead state.
Cancel
Command cancel takes a task ID and sends a cancelation signal to the goroutine processing the specified task.
You can obtain the task ID by running ls command.
The task should be in "in-progress" state. Handler implementation needs to be context aware in order to actually stop processing.
Example:
asynq cancel bnogo8gt6toe23vhef0g
Config File
You can use a config file to set default values for the flags. This is useful, for example when you have to connect to a remote redis server.
By default, asynq will try to read config file located in
$HOME/.asynq.(yaml|json). You can specify the file location via --config flag.
Config file example:
uri: 127.0.0.1:6379
db: 2
password: mypassword
This will set the default values for --uri, --db, and --password flags.